Delving into the mechanics of a garage door opener, this blog will elucidate how these everyday devices function to conveniently lift and lower your garage door.
A garage door opener, a device many homeowners use daily, operates on a simple yet effective mechanism. At its core, a garage door opener is a motorized device that opens and closes garage doors, typically controlled by switches on the garage wall or by remote controls carried by the owner.
The magic of its operation lies in a combination of several components: a motor, a trolley, a carriage, a drawbar, and a remote control system. This article will delve into the specifics of how each component works together to make the operation of your garage door as smooth as possible.
So, if you’re looking to understand the intricacies of your garage door opener or considering a DIY repair, you’re in the right place.
Key takeaways:
- Belt Drive Openers: Quiet and smooth operation for attached garages.
- Chain Drive Openers: Reliable and economical, suitable for detached garages.
- Screw Drive Openers: Sturdy, low maintenance, and good for extreme climates.
- Direct Drive Openers: Super quiet and durable, with minimal moving parts.
- Jackshaft Openers: Mounts on the wall, saves overhead space for heavy doors.
Types of Garage Door Openers

Diving straight into the heart of the topic, five primary types dominate the garage door opener market.
First up, Belt Drive Openers maximize silence and smooth operation, making them suitable for garages attached to living areas. They utilize a rubber belt, a feature that significantly reduces noise but bumps up the price a notch.
Next, Chain Drive Openers, a widely used class owing to their reliability and affordability. As the name suggests, these employ a metal chain, trading off silence for a more economical price.
For the endurance lovers, Screw Drive Openers offer a sturdy option. These use a threaded steel rod to move the trolley, ensuring extended longevity at the cost of slightly higher noise levels.
Then we have Direct Drive Openers, where the motor itself moves the trolley. This fascinating technology provides super quiet operation and minimal moving parts, therefore reduced maintenance.
Lastly, Jackshaft Openers mount on the garage wall next to the door, freeing up ceiling space. These are an excellent choice for giant, weighty doors or garages where overhead room is at a premium.
Understanding these types can help in making an informed choice best fitting personal needs and preferences.
Belt Drive Garage Door Openers
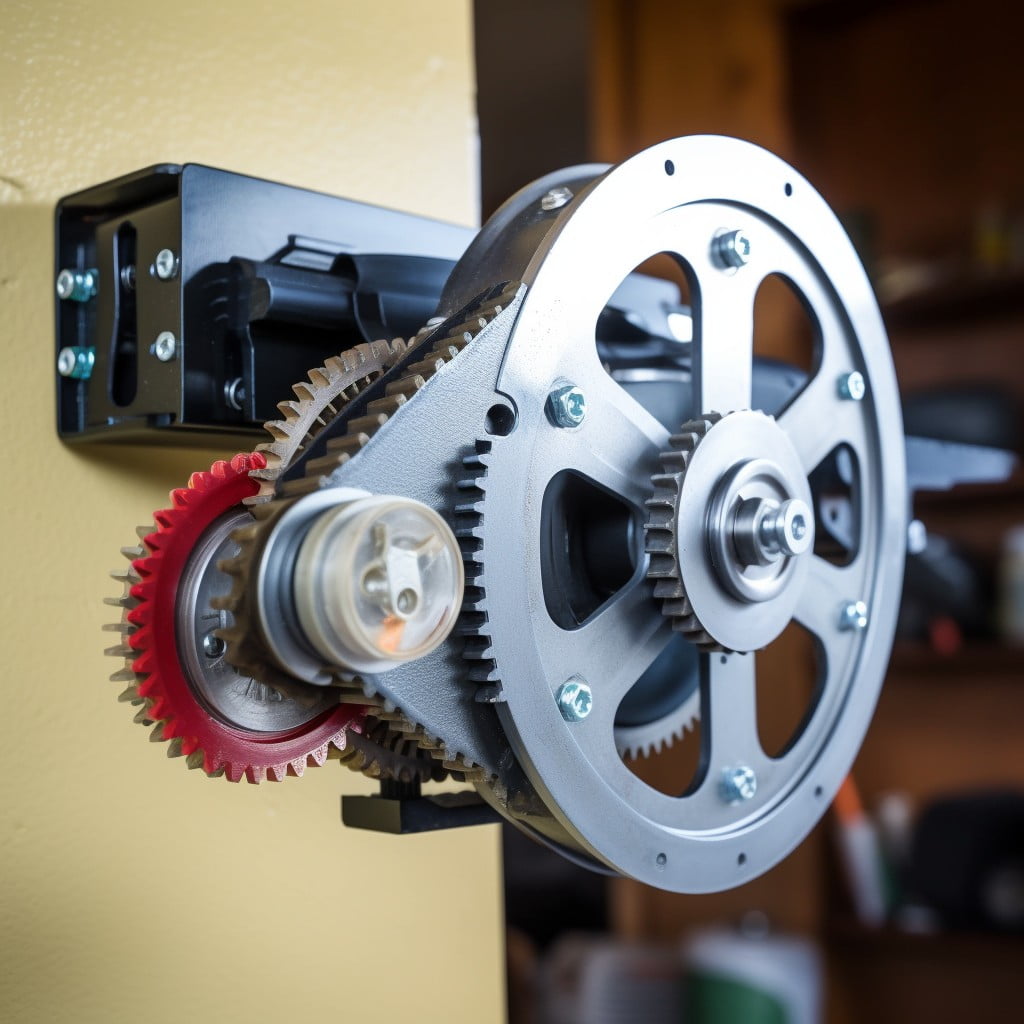
Characterized by their smooth and quiet operation, these openers utilize a belt made of reinforced steel or fiberglass to move the garage door. Unlike other types of openers, they require minimal maintenance due to the absence of metal-on-metal contact, reducing wear and tear. The strong composition of the belt makes it highly durable, while its flexibility allows for smooth door movement.
In terms of cost, they are often priced higher but offer long-term benefits like reduced noise and lower maintenance costs. Great for homes with living spaces above or adjacent to the garage, their near-silent operation won’t disturb those in close proximity.
Chain Drive Garage Door Openers
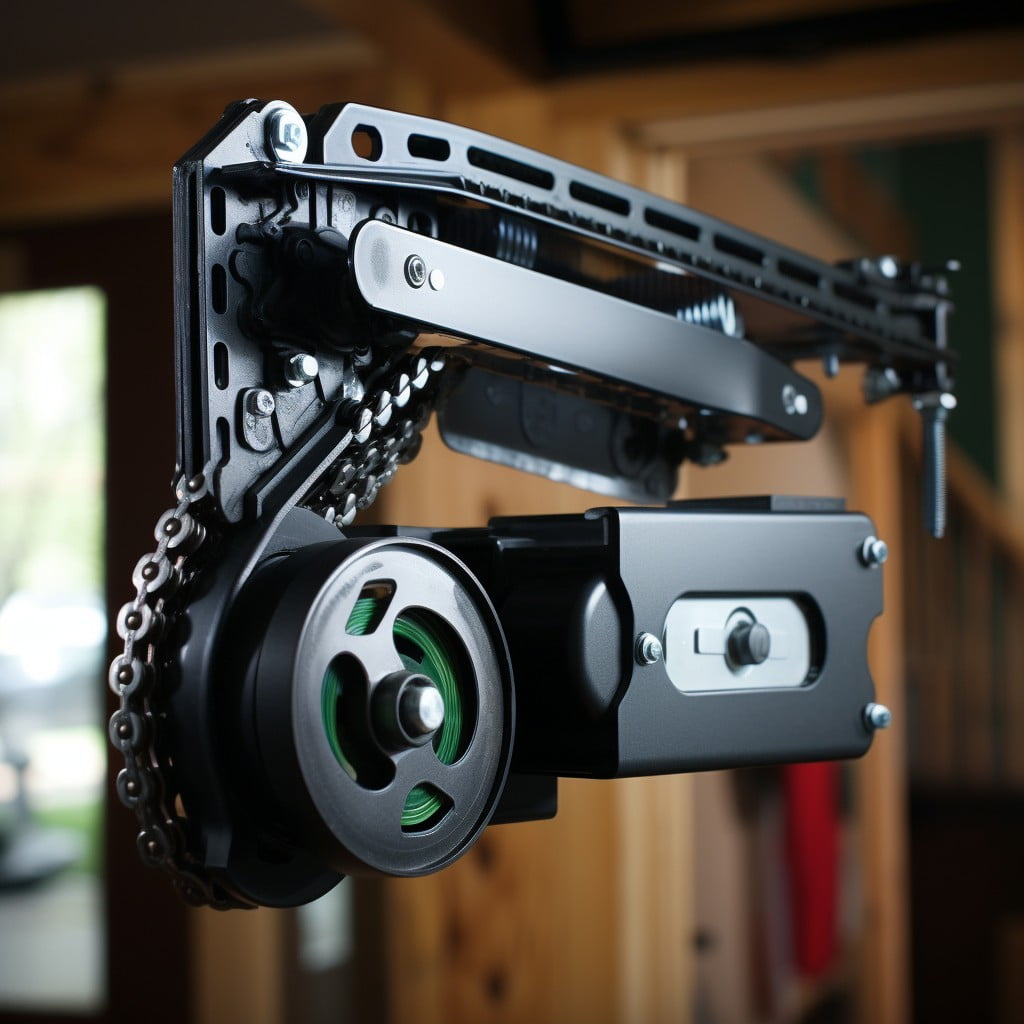

Dependable and robust, these openers rely on a metal chain to push or pull a trolley that moves the door up and down. Resilience in the face of varying weather conditions is a significant advantage, making these systems suitable for extreme climates. Nevertheless, keep in mind that this strength comes with an increased noise level, making them better suited for detached garages.
The mechanism includes a motor that turns gears, moving the chain attached to the J-arm, which is linked to the door. This system represents an excellent example of the conversion of rotational motion to linear motion, harnessing the power of the motor to facilitate the opening and closing of heavy garage doors.
Plus, chain drive units are relatively easy to maintain. Regular lubrication will keep the chain in optimal shape, increasing the lifespan of your opener. Yet, while all these features make chain-openers sought after, they may not be the best choice for those seeking quiet operation.
Screw Drive Garage Door Openers
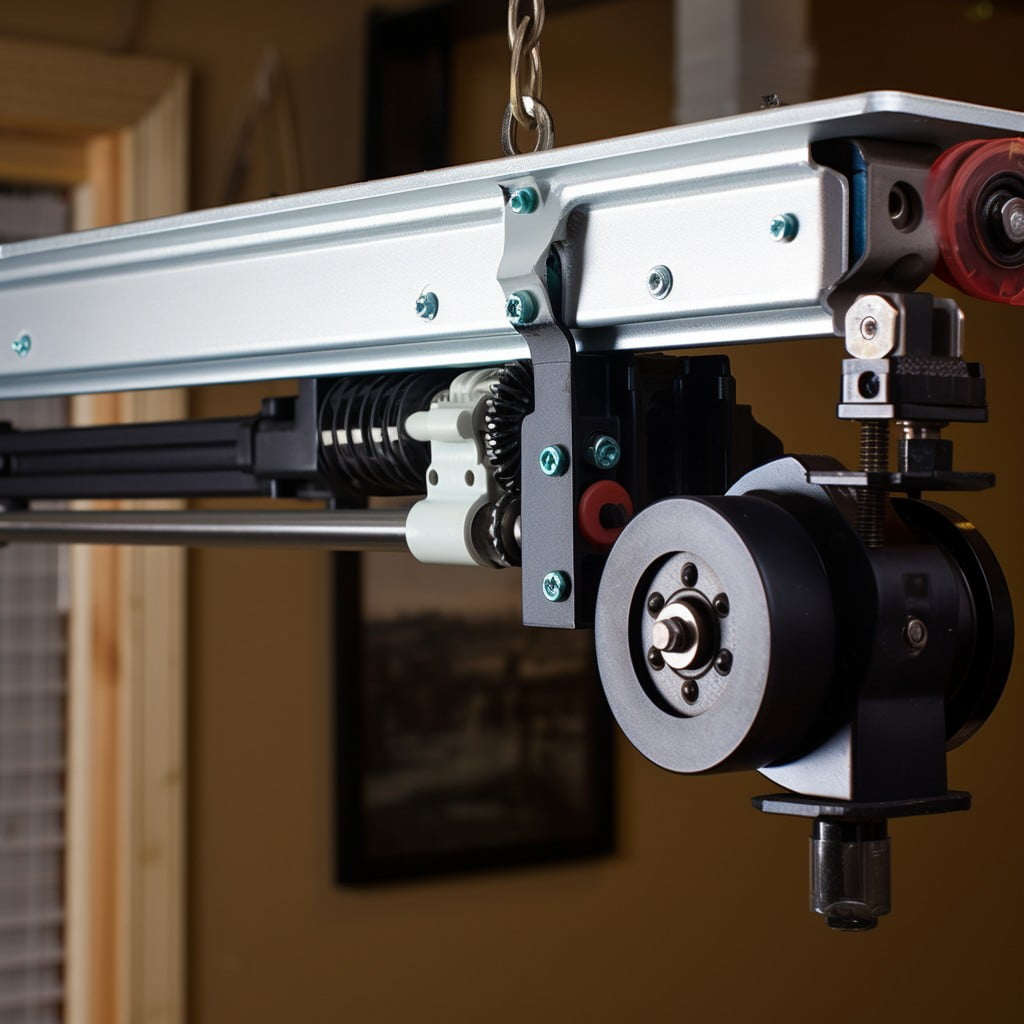
Benefitting from fewer moving parts, these openers function through a threaded steel rod that rotates, moving the trolley to open or close the door. They offer simplicity and reliability due to their straightforward mechanical design, which reduces potential breakdown points.
Screw drive openers are also inherently balanced since the weight of the door is evenly distributed along the threaded rod. This helps to prevent premature wear and tear and can result in a longer lifespan for the opener.
While slightly noisier than belt drive options, they are quieter than chain drive openers and are a strong choice for heavy or oversized doors. The chief drawback to consider is that changes in temperature could affect operation, meaning these openers may not be the best choice for regions with extreme climates. Additionally, they generally require more regular maintenance than some other types.
Direct Drive Garage Door Openers
With a unique mechanism compared to its counterparts, a direct drive opener is crafted with only one moving part – the motor. Its innovative design offers a quieter, smoother operation since it necessitates fewer moving parts, reducing the chance of malfunction due to wear and tear.
This system operates by the motor gliding along a stationary chain that’s encased within an overhanging rail, moving the garage door with it. The motor, acting as both the trolley and the power source, provides the ample force needed to lift and lower the door. The absence of belts, chains, or screws, equals less vibration resulting in minimal noise.
Another appreciable attribute of direct drive openers is their durability. The lesser number of moving components means less maintenance over the lifespan of the opener. Meanwhile, its outstanding power makes it suitable for lifting even heavy garage doors.
Moreover, many models come with built-in safety features. For instance, some are designed to stop if an obstacle is encountered, preventing harm or damage.
Though they may seem expensive upfront, their long-term benefits in the form of efficiency and durability make them a worthy investment in many garages.
Jackshaft Garage Door Openers
Unlike traditional garage door openers, these models are mounted on the wall beside the garage door. An ideal choice for garages with high or sloping ceilings, Jackshaft garage door openers function by turning the torsion bar to raise and lower the door.
They ensure that overhead space is not wasted and lessen the noise factor significantly. Their working mechanism makes use of a powerful DC motor that moves the torsion springs, the force responsible for the heavy lifting. Security is heightened with their ability to operate even during a power outage, thanks to an optional battery backup system.
Although they tend to be more expensive than their counterparts, the range of advantages they offer can justify the cost for many homeowners.
Anatomy of a Garage Door Opener
The main components of a garage door opener consist of the motor, torsion springs, drive unit, chain, pick-up arm, bracket, photo eyes, and an emergency release rope.
The motor, powered by electricity, sparks the opening or closing motion. This happens when it spins the drive unit, typically a small toothed wheel. This in turn, makes the chain or belt move, initiating the opening or closing process.
Torsion springs aid this process, counterbalancing the door’s weight. This makes the door seem lighter, allowing the motor to operate efficiently without overload.
The chain or belt, connected to the drive unit, moves along a rail between the power unit and the door. The chain’s movement, influenced by the drive unit, guides the door’s motion.
The pick-up arm, attached to the chain and the door, is the link between them, ensuring they move in sync.
Brackets affixed to the garage floor and ceiling hold the rail with the moving chain or belt in place.
Photo eyes act as safety devices. Positioned on either side of the door close to the floor, they use infrared beams to detect obstacles in the door’s path.
The emergency release rope, usually a red cord hanging from the rail, allows manual operation of the door in case of power failure or malfunction. Pulling the cord disengages the trolley, facilitating manual lifting or lowering of the door.
Parts of a Garage Door Opener
Central to any opener is the motor, a powerhouse that initiates the opening and closing of a garage door. Speed and horsepower may vary, but its function remains steady – to set the system in motion.
Torsion springs are next in line. Working hand in hand with the motor, they store mechanical energy and generate the force required to lift the door. Springs do the heavy lifting, but they’re controlled by the drive unit.
Drive units include chain, belt, screw, direct, and jackshaft drives. They control the movement of the garage door, working kind of like a transmission in a car, regulating force and speed.
The chain is used by many traditional garage door openers, acting like a bicycle chain, they engage the motor to start the movement of the door.
The pick-up arm connects the opener to the garage door. Although not flashy, it’s significant. It’s the bridge between the motor and the door, and without it, no movement would be possible.
The photo eyes, a safety feature of the system, use invisible beams to detect any object in the way of the shutting door, stopping the door from harming a person or damaging property.
The bracket holds the entire system together, housing the various moving parts and ensuring they’re secure. It’s like an umbrella under which all other parts operate.
Lastly, the emergency release rope. This manual override, usually a red rope hanging from the opener, allows to disconnect the door from the opener and operate it manually in case of a power outage or a malfunction.
Motor
The motor is pivotal to a garage door opener’s operation as it generates the power needed to lift and lower the door. It’s typically housed within the main unit and is either an AC (alternating current) or DC (direct current) model.
AC motors are reliable, but they operate at one fixed speed and can be a bit noisy. On the other hand, DC motors operate more quietly and allow for variable speed control, offering a smooth start and stop for the garage door, prolonging its lifespan.
The motor’s strength is commonly measured in horsepower (HP), with typical home garage door openers ranking from 1/2 HP to 1 1/2 HP. Bigger, heavier doors would necessitate a motor with more horsepower, ensuring the adequate power supply for efficient operation.
Torsion Springs
An integral part of any garage door opener, torsion springs counterbalance the weight of the door. Settled on a shaft above the door, these springs operate under high tension. As the door lowers, they wind up, storing energy. Then, when the opener signals the door to rise, this stored energy is released, helping the motor raise the door easier.
Torsion springs have a specific lifespan, measured in cycles of opening and closing. Typically, after about 10,000 cycles, wear and tear will set in, potentially leading to a snap. This situation demands immediate professional help, as repairing or replacing a broken spring is dangerous due to its high tension.
Regular maintenance and checks of torsion springs can help avoid unexpected breakages. Warning signs such as a slow opening process, visible gaps in the spring or a stopped door midway may indicate an issue with these crucial components. Remember, safety must always be paramount when dealing with these high-tension elements.
Drive Unit
The drive unit, commonly termed as the opener, is essentially the brains behind the entire operation. This key component, equipped with an internal computer, is responsible for sending signals to initiate moves of opening or closing. It receives prompts—from wireless remotes, keypads or wall-mounted buttons—to activate the motor, where the essence of the movement of your garage door lies.
Digging a bit deeper, the drive unit doesn’t directly move your door but manages the release of tension in its torsion springs. These springs hold potential energy when the door is down, and the release of this stored energy by the opener’s command is what primarily propels the door up or down.
Additionally, the drive unit also helps to calibrate the precise amount of force needed to perform these operations, ensuring a smooth function and avoiding any undue stress on the mechanism. This intelligent feature plays a pivotal role, especially during extreme weather conditions when the garage door might require a bit extra power to perform its function.
Lastly, the drive unit is equipped with safety features such as a reverse mechanism. This is activated when an obstruction is detected, preventing accidents. Safety sensors, also known as photo eyes, communicate with the drive unit to facilitate this. Hence, in a nutshell, the drive unit is the ultimate command centre controlling your garage door’s operations.
Chain
A significant component in many garage door openers, the chain operates in a mechanism akin to a bicycle chain. It’s primarily designed to lift or lower the garage door with the help of the motor, which sets the whole process in motion. As the motor turns the gear, it causes the chain to move, pushing or pulling the trolley depending on the direction the garage door needs to move.
This type often offers rugged durability and powerful performance, making it ideal for heavy or frequently used doors. However, compared to some other types, chain-drive system operates noisily, which might be a consideration if your garage is adjacent or below living spaces.
Regular maintenance of the chain, such as lubrication, ensures smooth operation and prolongs its lifespan, avoiding premature wear and tear. But over time, this essential component may stretch and require adjustment or replacement for optimal performance.
Pick-Up Arm
Bearing the vital role of connecting the carriage to the door, the pick-up arm stands as the middleman. It is responsible for transferring the force applied by the drive mechanism to actually move the door. It maintains a perpendicular position to the door to ensure smooth and even motion.
Do note that the pick-up arm requires regular maintenance to prevent rusting and ensure consistent performance. Lubricating this component periodically will prolong its lifespan and make opening and closing your garage door a seamless experience.
Additionally, the correct installation of the pick-up arm is quintessential. A misaligned arm may result in a strained motor, unbalanced movement of the door, or even more consequential damage to the garage door system. Therefore, whenever installing or adjusting the pick-up arm, consider enlisting professional help to avoid complications.
Bracket
The bracket, typically affixed securely on the garage door itself, plays a crucial role in the functioning of the garage door opener. It holds the end of the pick-up arm in position, connecting the opener to the door. During operation, forces exerted by the pick-up arm enable the motor to either pull the door up or let it down smoothly.
A few additional points to consider about the bracket:
- 1. It should be carefully installed and well-maintained to ensure optimal operation.
- 2. Common problems involve loosening of the bracket, resulting in less efficient door opening or closing. Regular check-ups should be in place to avoid such issues.
- 3. If the bracket becomes damaged, it’s recommended to replace it immediately to prevent further damage to other parts of the door opener.
- 4. Ensure all screws holding the bracket are fully tightened, but avoid overtightening to prevent damage to the door.
- 5. Most brackets are made of heavy-duty metal for long-lasting performance.
By paying close attention to the condition and position of your garage door opener’s bracket, you can ensure a smooth, efficient operation for years to come.
Photo Eyes
Located at the base of your garage door are two small devices known as photo eyes. These elements form an integral part of the safety system of your opener. Their primary role is to send an infrared beam across the length of the door’s path. If anything interrupts this beam — be it an object, person, or pet — while the door is in operation, the photo-eyes send a signal to the opener to reverse the closing action, preventing any potential accident.
It’s important to ensure these units are properly aligned with one another. If they’re not, it may cause false signals, leading your door to stop or reverse unexpectedly. Also, keep the photo eyes clean from dirt or dust accumulation for smooth functioning. Regular maintenance with a gentle wipe can prevent unwanted interference with the infrared beam.
The practical positioning about six inches off the ground optimizes their ability to detect objects. This clever design is just another example of how your garage door opener works to secure and streamline your day-to-day operations.
Emergency Release Rope
The emergency release rope often has a red handle and is positioned in a convenient location to be easily pulled in the event of a power failure or malfunction with your opener. This reverts the function of the garage door back to manual mode, allowing homeowners to manually open and close the garage door when required.
The release rope disengages the carrier from the track, permitting manual operation. Remember to resume automatic function, reengage the system by pulling the rope downwards towards the door. It’s also important to note that the emergency release should not be used unless the door is fully closed, or supported, to prevent any potential injuries or damage due to the weight of the garage door.
Functionality of a Garage Door Opener
In essence, the operation of a garage door opener begins when you press the remote control button. This action sends a signal to the motor inside the garage door opener unit, prompting it to start. The motor then engages the drive unit, which is either a belt, chain, or screw-based system depending on the type of garage door opener you have.
As the motor turns the drive unit, the chain (or belt or screw) is moved. This chain is directly connected to the garage door via a pick-up arm and bracket. As the chain moves, it pulls or pushes the pickup arm, which in turn moves the door up or down.
It should be noted that the heavy lifting is not done by the motor but by the torsion springs. These springs store mechanical energy when the door is closed. This energy is then released when the door needs to be opened, doing most of the heavy lifting, significantly reducing the strain on the motor.
Furthermore, the system is equipped with photo eyes, which are critical safety features. These are sensors placed about six inches off the ground on either side of the door that detect if something or someone is in the door’s path when it’s closing. If the beam between these sensors is broken, the door will instantly stop closing and reverse direction.
Lastly, every garage door opener features an emergency release rope – generally a brightly colored rope that hangs from the pick-up arm. This rope disconnects the door from the opener, allowing for manual operation in times of power outages or motor failure.
How Do Garage Door Opener Parts Work Together?
Starting from the remote control or wall switch, a signal is sent to the motor housed on top of the garage. This motor then spins gears within the drive unit that is attached to a chain, belt, or rod depending on the type of garage door opener you have. The chain initiates the lifting of the garage door by the pivotal pick-up arm that’s fastened to the door.
The vital counterbalance during this motion is offered by the torsion springs, which functionally reduce the weight of the door for the easy lifting process. The door is guided on its rails by the brackets avoiding misalignment.
For safety, two photo eyes are strategically positioned at the bottom of the door track on each side. They transmit an invisible beam across, which if broken by any object, immediately signals the motor to stop and reverse the garage door. This prevents any damage or harm.
Lastly, in case of any malfunction or a power outage, the emergency release rope aids in manually operating the door, disengaging the motor from the door.
These components work together seamlessly, giving you the convenience of an efficiently functioning garage door opener.
Troubleshooting Common Garage Door Opener Problems
1. Not Opening or Closing: Check the photo-eyes for alignment, obstructions, and clean them if necessary. Also, look at the garage door’s torsion springs for any signs of wear or breakage.
2. Door Reverses Immediately: This usually points to a problem with the limit settings, which control the point where the door should stop in its upward or downward travel.
3. Remote Control Not Working: Check batteries first, then the antenna on the motor unit to see if it’s damaged or blocked. If problems persist, you might need to reprogram the remote.
4. Unresponsive Even From Wall Switch: Check connections and wiring. But if everything seems OK, the motor unit might be burned out and needs replacing.
5. Noisy Operation: This could be due to worn-out parts, loose hardware, or lack of lubrication. Regular maintenance can avoid most of these issues.
6. Door Doesn’t Seal at The Bottom: Adjust the close limit switch. If that does not fix the issue, replace the weatherstripping at the bottom of the door.
7. Opener Runs, But Door Doesn’t Move: Check the disconnect switch. This must be attached to the motor to control the door.
FAQ
How does a garage door opener communicate?
A garage door opener communicates via a remote control that emits a radio wave on a specific frequency, which is then detected by a built-in receiver in the garage door opener causing it to either open or close the door as needed.
How does a garage door opener know when to stop?
A garage door opener is guided by set-limit switches, which instruct the motor to halt operations, either when opening or closing the door.
What are the mechanisms for garage door openers?
The three main types of garage door openers are chain drive, which are inexpensive but noisy, belt drive, and screw drive.
What components are essential for a garage door opener's functionality?
A garage door opener's functionality primarily relies on essential components such as a motor, gear set, chain or belt drive, and remote control or wall-mounted switches.
How do safety features in modern garage door openers operate?
Modern garage door openers operate safety features primarily through two mechanisms: infrared sensors that halt the door if something crosses the path, and a force-sensing feature to reverse the door if it contacts an object during closing.
Which type of garage door opener provides the highest level of efficiency and why?
The belt-driven garage door opener provides the highest level of efficiency due to its quiet operation, minimal maintenance, and long lifespan.